Best Hotel Operating Systems A Deep Dive
The best hotel operating systems are crucial for modern hospitality. They underpin everything from guest check-in to revenue management, and their evolution mirrors the broader technological advancements in the industry. From property management systems to central reservation and revenue management tools, these systems significantly streamline hotel operations, leading to improved efficiency and enhanced guest experiences. This exploration delves into the core functionalities, key features, and integration strategies, providing a comprehensive overview of the best systems available.
Different types of hotel operating systems, including PMS, CRS, and RMS, cater to various needs. A comparative analysis, including pricing models and vendor information, will help readers understand the strengths and weaknesses of each system type. The analysis also explores the implications of cloud-based versus on-premise systems, examining their respective advantages and disadvantages across different hotel sizes and types.
Introduction to Hotel Operating Systems
Hotel operating systems are the backbone of modern hospitality, managing the entire guest experience from booking to check-out. These systems encompass a wide range of functionalities, automating tasks and streamlining operations to enhance efficiency and profitability. Their evolution reflects the broader advancements in technology within the hospitality industry, enabling hotels to cater to an increasingly demanding and digitally savvy clientele.
Hotel technology has evolved significantly, moving from manual processes to integrated software solutions. Early systems focused primarily on inventory management and room assignments. The introduction of property management systems (PMS) marked a crucial turning point, centralizing data and improving operational efficiency. Subsequent developments brought central reservation systems (CRS) and revenue management systems (RMS), further enhancing revenue generation and optimizing pricing strategies. These advancements have allowed hotels to provide a more personalized and seamless experience for guests, while also improving the efficiency of hotel staff.
Types of Hotel Operating Systems
Hotel operating systems are categorized into various types, each with specific functionalities tailored to particular aspects of hotel management. These systems work together to create a holistic and efficient operation.
Property Management Systems (PMS), Best hotel operating systems
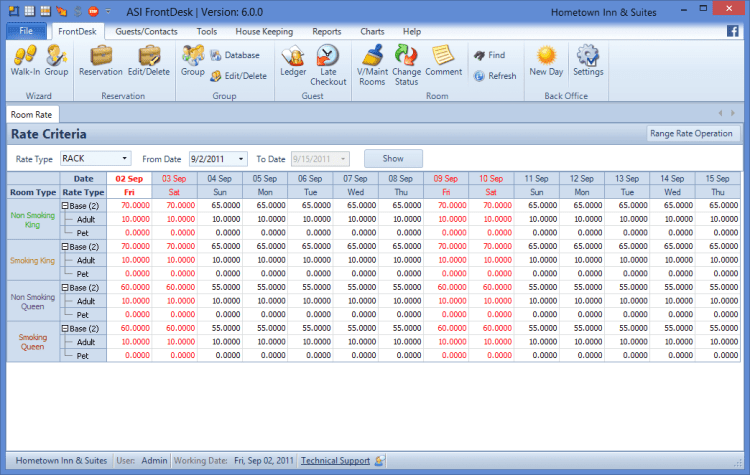
Property management systems (PMS) are the core of hotel operations, handling crucial tasks such as room assignments, guest check-in/check-out, inventory management, and guest communication. PMSs play a vital role in the smooth functioning of the entire hotel, ensuring accurate record-keeping and efficient service delivery. A well-implemented PMS provides real-time data on room availability, guest preferences, and operational metrics, allowing for better decision-making and resource allocation.
Central Reservation Systems (CRS)
Central reservation systems (CRS) are crucial for managing online bookings and reservations across multiple hotels. They act as a central hub for accepting bookings from various channels, ensuring seamless distribution and coordination of reservations across different hotels. A robust CRS helps hotels maintain accurate inventory records, manage pricing strategies, and improve the overall guest booking experience.
Revenue Management Systems (RMS)
Revenue management systems (RMS) are designed to optimize revenue generation by dynamically adjusting pricing based on factors such as demand, seasonality, and competitor pricing. RMSs analyze historical data and market trends to determine optimal pricing strategies for rooms, packages, and other services. They allow hotels to maximize revenue potential by strategically adjusting prices in real-time, ensuring profitability and maximizing revenue generation.
Comparison of Hotel Operating Systems
| System Type | Key Features | Pricing Model | Vendor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Property Management System (PMS) | Room assignments, guest check-in/out, inventory management, guest communication, reporting | Typically subscription-based, with tiered pricing based on features and hotel size | e.g., Opera, Micros, HotelREZ |
| Central Reservation System (CRS) | Online booking management, multi-hotel distribution, inventory control, channel management | Usually subscription-based, with pricing varying by the number of properties and booking channels | e.g., Sabre, Amadeus, Travelport |
| Revenue Management System (RMS) | Dynamic pricing, demand forecasting, competitor analysis, pricing optimization, revenue forecasting | Subscription-based, with pricing models often tailored to the specific needs of the hotel | e.g., HotelDruid, YieldWise, RevPar |
Key Features and Benefits
Hotel operating systems are crucial for optimizing efficiency and enhancing the guest experience in the hospitality industry. Modern systems provide a comprehensive suite of tools to manage various aspects of a hotel’s operations, from reservations and check-in to housekeeping and financial reporting. This section details essential features and contrasts the benefits of different operating systems, considering the varying needs of hotels of different sizes and types.
Essential Features of Top-Performing Systems
Top-performing hotel operating systems share several key features that drive efficiency and guest satisfaction. These include robust reservation management, seamless check-in and check-out processes, integrated property management, and comprehensive reporting tools. Advanced systems often include features like guest history tracking, predictive analytics, and personalized service recommendations. These features allow hotels to better understand guest preferences, anticipate needs, and personalize the guest experience.
Impact on Efficiency and Guest Experience
Efficient hotel operating systems directly impact both operational efficiency and the guest experience. Automated check-in/check-out procedures reduce wait times and streamline the guest journey. Real-time inventory management prevents overbooking and ensures availability for guests. Comprehensive reporting allows hotels to identify areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation. Moreover, personalized recommendations and guest history tracking enhance guest satisfaction by creating a more tailored and memorable experience. This leads to increased customer loyalty and positive reviews.
Comparison Across Hotel Sizes and Types
The optimal hotel operating system varies based on hotel size and type. Small boutique hotels might benefit from a user-friendly system with streamlined reservation and guest management tools. Larger resorts or chains often require a more sophisticated system with advanced features like centralized inventory management, comprehensive reporting, and robust security protocols. Specialized hotels, such as spas or conference centers, may need systems tailored to specific operational requirements. For example, a conference center will require advanced scheduling and meeting room management tools.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Systems: A Comparative Analysis
Choosing between cloud-based and on-premise hotel operating systems involves weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each. A comparison table highlights crucial aspects to consider.
| Feature | Cloud-Based | On-Premise | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Software hosted on a remote server, accessible via the internet. | Software is installed and maintained on the hotel’s servers. | Cloud-based offers flexibility and scalability, while on-premise provides more control. |
| Cost | Typically lower initial cost, with ongoing subscription fees. | Higher upfront investment, but lower ongoing costs. | Long-term costs can vary depending on usage and feature needs. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to accommodate business growth. | Scaling requires significant infrastructure upgrades. | Cloud-based scaling is often more straightforward. |
| Maintenance | The vendor manages system maintenance and updates. | Hotel staff or the IT department handles maintenance and updates. | Cloud-based solutions minimize internal IT burden. |
| Security | Relies on vendor security protocols. | The hotel’s security measures protect the system. | Security responsibility depends on the deployment model. |
Integration and Interoperability: Best Hotel Operating Systems

Source: unifocus.com
Modern hotel operations rely heavily on interconnected systems. Effective integration between various software solutions, including hotel operating systems (POS), property management systems (PMS), and revenue management systems (RMS), is critical for streamlined workflows and enhanced guest experiences. This interconnectedness facilitates the efficient flow of information, enabling hotels to optimize their operations and maximize profitability.
Importance of Seamless Integration
Seamless integration between hotel operating systems and third-party applications is paramount for efficient data management and operational effectiveness. By connecting different systems, hotels can eliminate data silos, ensuring that all departments have access to the most up-to-date information. This leads to reduced errors, faster response times, and improved decision-making across the entire organization.
Impact on Data Management and Operational Efficiency
Integrated systems significantly enhance data management. Real-time data exchange between systems allows for accurate inventory tracking, precise room assignments, and timely guest service updates. This seamless flow of information minimizes manual data entry, reducing the potential for errors and freeing up staff to focus on other critical tasks. Operational efficiency is boosted by automated processes and real-time visibility into various aspects of the hotel’s performance. Improved forecasting and better control over resources are also key benefits.
Examples of Successful Integrations
Numerous successful integrations demonstrate the power of interconnected systems. A hotel chain might integrate its PMS with a loyalty program platform, enabling automated points accumulation and personalized offers for frequent guests. Similarly, integrating the hotel’s POS system with a restaurant management system allows for seamless order processing and accurate inventory control across the entire property. Furthermore, connecting the hotel’s energy management system with the PMS allows for real-time tracking of energy consumption, leading to potential cost savings and environmental benefits. Another example is integrating with online travel agencies (OTAs) to automatically update room availability and pricing in real-time.
Diagram of Interconnected Hotel Systems
The following diagram illustrates the interconnectedness of various hotel systems, showing the flow of data and communication between different components:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Guest Portal | | Property Management System (PMS) | | Revenue Management System (RMS) |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| | | |
| | | |
| Guest requests | Room assignments, | Pricing, forecasting |
| Booking changes | inventory updates, | Demand analysis |
| Feedback | guest details | Real-time updates |
| | | |
V V V
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Point of Sale (POS) | | Accounting System | | Guest Relationship Management (CRM) |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| | | |
| Order processing | Financial reporting | Guest communication |
| Payment processing | Cost analysis | Personalized offers |
| | | |
V V V
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Energy Management | | Maintenance System | | Security System |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| | |
| Energy consumption | Maintenance requests | Access control |
| Monitoring | Work order tracking | Security alerts |
| | | |
This diagram represents a simplified model. Specific connections and details may vary based on the hotel’s chosen technologies and their specific configurations.
User Interface and Experience

Source: intetics.com
A user-friendly interface is paramount for hotel staff using operating systems. Intuitive design significantly impacts employee satisfaction and operational efficiency. A well-designed system streamlines tasks, reduces errors, and ultimately enhances the guest experience.
Importance of Intuitive Interfaces for Staff
Effective hotel operating systems prioritize ease of use for staff. This translates to faster task completion, reduced training time, and decreased errors. Staff members who can easily navigate and utilize the system are more likely to be satisfied and productive. Minimizing the learning curve and complexity enhances overall operational efficiency.
Contribution to Employee Satisfaction and Operational Efficiency
A user-friendly interface directly impacts employee satisfaction. When staff find the system easy to use, they experience less frustration and stress. This leads to improved morale, reduced staff turnover, and increased employee retention. Streamlined workflows, facilitated by intuitive interfaces, directly enhance operational efficiency by minimizing errors and maximizing productivity.
Examples of Effective User Interface Designs
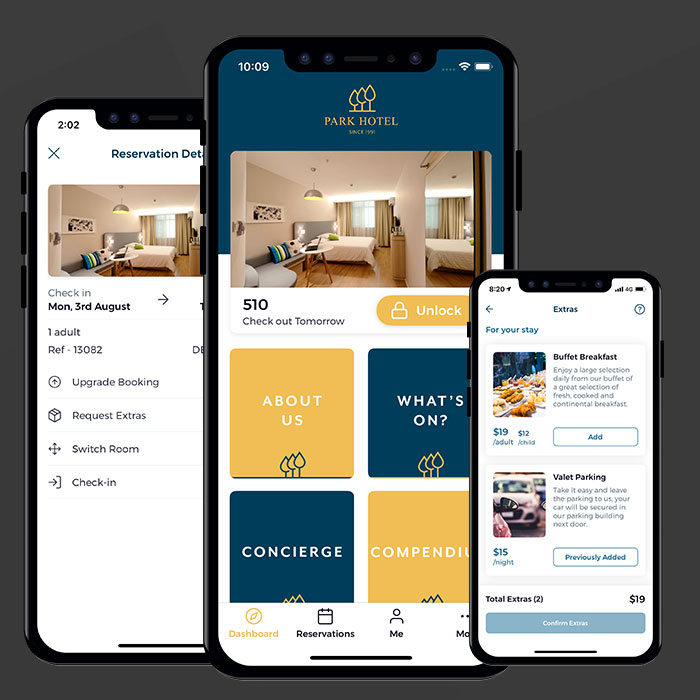
Various interface design strategies can be implemented to support hotel operations. Visual clarity, logical organization, and intuitive navigation are crucial. Color-coding, well-defined icons, and clear labels enhance system usability. For example, a system displaying room availability with color-coded indicators (green for available, red for occupied) is more efficient than a system that requires extensive searching. Another example is a booking system with clear visual cues to indicate the status of a reservation (e.g., confirmed, pending, cancelled). Similarly, a dashboard displaying key performance indicators (KPIs) at a glance, such as occupancy rates and revenue trends, allows staff to quickly assess and respond to operational needs.
Hotel Operating System Dashboard Mock-up
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Top Section (Dashboard) | Displays key performance indicators (KPIs) at a glance, including occupancy rate, revenue, average daily rate (ADR), and other relevant metrics. This provides a quick overview of the hotel’s performance. Real-time data updates are essential for informed decision-making. |
| Room Availability Grid | Visually represents room availability. Color-coding (e.g., green for available, red for occupied) simplifies the process of identifying vacant rooms. Room details, including amenities and pricing, can be easily accessed by clicking on a room. |
| Guest Management Section | Allows for easy management of guest information, including arrival and departure details, special requests, and contact information. Filtering options and search capabilities enhance the efficiency of locating guest records. |
| Reservation Management Section | Displays current reservations, allowing staff to easily modify, cancel, or update bookings. A clear indication of reservation status (e.g., confirmed, pending, cancelled) is vital. |
| Reporting Tools | Offers customizable reporting options to generate various reports, such as revenue reports, occupancy reports, and guest profiles. This section supports data-driven decision-making. |
“A well-designed user interface can significantly reduce the time and effort required to complete tasks, thereby improving efficiency and reducing the potential for errors.”
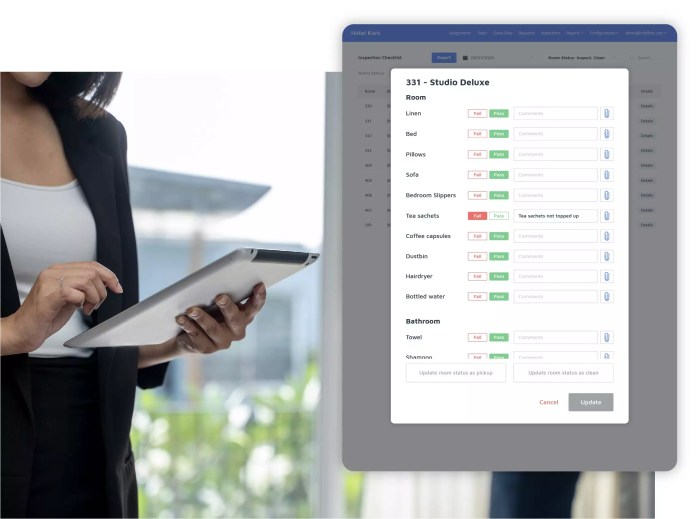
Implementation and Maintenance
Source: vouch-technologies.com
Implementing a new hotel operating system requires careful planning and execution. This phase encompasses the transition from the existing system, training staff on the new platform, and ensuring ongoing support and maintenance to maximize efficiency and minimize disruption. Effective implementation directly impacts the hotel’s operational success and guest experience.
Steps Involved in Implementing a New System
The implementation process typically follows a phased approach. First, detailed system configuration and integration with existing hotel technologies are critical. This includes mapping data flows, defining user roles, and setting up necessary interfaces. Second, rigorous testing is essential to validate functionality, identify potential issues, and refine the system before its full deployment. Third, a phased rollout ensures a controlled introduction, allowing for adjustments and minimizing disruption to daily operations. Finally, a comprehensive training program is vital for staff to efficiently utilize the new system.
Importance of Staff Training
Thorough training is paramount for successful system adoption. A well-structured training program familiarizes staff with the new system’s functionalities, procedures, and best practices. This reduces errors, improves efficiency, and promotes user confidence. Training should cover practical applications, troubleshooting, and system limitations, ensuring staff members are equipped to handle various situations. Examples of training modules could include check-in/check-out procedures, room management, and reservation handling.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support Requirements
Ongoing maintenance and support are essential for a hotel operating system. This includes regular software updates, security patches, and performance monitoring. Proactive maintenance prevents potential issues and ensures optimal system performance. System administrators should regularly monitor system logs, performance metrics, and user feedback to address any emerging problems. Having dedicated support personnel or access to reliable technical support is crucial for timely assistance and resolution of issues.
Migrating from an Older System to a New One
A structured migration plan is essential for a smooth transition.
A well-defined migration plan Artikels the steps, timelines, and responsibilities for each phase of the transition.
- Assessment and Planning: Thoroughly analyze the existing system and identify data that needs to be migrated. Create a detailed project plan that includes timelines, resource allocation, and potential risks.
- Data Migration: Carefully transfer data from the old system to the new one. This involves data validation and verification to ensure accuracy and completeness. Consider using data migration tools to automate the process.
- System Configuration: Set up the new system according to the hotel’s specific needs and configurations. This includes configuring user access levels, defining workflows, and integrating with other systems.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the new system to ensure all functionalities work correctly. This includes testing with real-world scenarios and user data. Identify and address any issues.
- Phased Rollout: Gradually transition to the new system, starting with a pilot group or a specific department. This allows for adjustments and feedback before a full rollout to all users.
- User Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training to staff on the new system. Establish clear communication channels for ongoing support and assistance.
- Post-Implementation Review: Evaluate the success of the migration, identify areas for improvement, and document lessons learned for future projects.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
Hotel operating systems are constantly evolving to meet the demands of a dynamic hospitality landscape. Technological advancements are driving significant changes, impacting how hotels operate, interact with guests, and manage their resources. This section explores the key emerging trends and the potential future of these systems.
The future of hotel operating systems is intertwined with the broader trends in technology, particularly artificial intelligence and machine learning. These advancements promise to optimize various aspects of hotel operations, from streamlining guest check-in and room assignments to predicting and addressing guest needs proactively. Innovative features are being developed to enhance efficiency and deliver a superior guest experience.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize hotel operations. Predictive analytics can forecast demand, optimize pricing strategies, and anticipate guest needs. Intelligent chatbots can handle routine inquiries, freeing up staff for more complex tasks. Personalized recommendations for dining, activities, and amenities can enhance the guest experience. Examples of this include AI-powered systems that automatically adjust room temperatures based on occupancy and guest preferences.
Enhanced Guest Experience Features
Hotels are increasingly focusing on creating personalized and seamless experiences for guests. This includes incorporating technologies like augmented reality (AR) for virtual tours of the property or interactive maps. AI-powered concierge services can provide personalized recommendations and support. Interactive displays in guest rooms allow guests to control lighting, temperature, and entertainment options. These features improve the overall experience and create a more memorable stay.
Cloud-Based Solutions and Scalability
Cloud-based operating systems offer increased scalability and flexibility, enabling hotels to adapt to fluctuating demands and changing market conditions. Data security and accessibility are paramount considerations in this transition. The accessibility of real-time data from across various departments allows for more efficient decision-making and improved communication within the hotel. This is especially important for smaller hotels that need to operate with a limited staff and budget.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Integrating AI-driven automation into existing workflows can streamline various tasks. This includes automated check-in/check-out processes, smart room management, and optimized inventory control. Real-time data analysis allows for better forecasting and proactive problem-solving. Improved operational efficiency leads to reduced costs and increased profitability. For example, real-time inventory tracking helps hotels minimize waste and maximize the utilization of resources, leading to cost savings.
Security and Data Privacy Enhancements
The growing reliance on data within hotel operating systems necessitates robust security measures. Data encryption, access controls, and compliance with relevant privacy regulations are critical. Maintaining guest trust and complying with regulations like GDPR are crucial for the long-term success of hotels using these systems. These systems must have the appropriate measures in place to protect guest data and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Summary
In conclusion, the best hotel operating systems are powerful tools for optimizing hotel operations. By carefully evaluating features, integration capabilities, and user experiences, hotels can choose systems that align with their specific needs and contribute to overall operational efficiency. Future trends, such as the increasing role of AI and machine learning, will further shape the evolution of these systems, promising even greater advancements in guest experience and operational effectiveness. Understanding these intricacies is key for hotels looking to remain competitive in the evolving hospitality landscape.