Best Hotel Software A Comprehensive Guide
Best hotel software is essential for modern hospitality. It streamlines operations, boosts revenue, and elevates the guest experience. This guide delves into various types of software, from property management to revenue optimization, exploring their key features and the evolution of this crucial technology. We’ll analyze selection criteria, highlighting budget considerations, operational needs, and integration capabilities. Understanding the benefits of hotel software is key to maximizing efficiency, guest satisfaction, and staff productivity. We’ll also examine implementation strategies, discuss emerging trends like cloud-based solutions and AI, and conclude with case studies of successful software deployments.
Choosing the right hotel software can significantly impact a property’s success. This in-depth exploration will empower hoteliers to navigate the complexities of the market and make informed decisions. We’ll present a detailed overview of different software types, comparing their features, functionalities, and pricing models. This will provide a solid foundation for understanding the various options available. The selection process is crucial, and we’ll offer practical advice on evaluating your needs, prioritizing features, and considering integration. Ultimately, this guide provides a comprehensive resource for hotels seeking to optimize their operations and elevate their guest experience.
Hotel Software Overview
Hotel software plays a crucial role in the modern hospitality industry, streamlining operations and enhancing guest experiences. From basic property management to sophisticated revenue optimization, these systems are essential for hotels of all sizes. This overview explores the various types of hotel software, their functionalities, and their evolution.
The proliferation of technology has led to a wide array of hotel software solutions, tailored to specific needs and budgets. This detailed look at the different types of hotel software, including their features and pricing, will provide a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape and future trends.
Property Management System (PMS)
Property Management Systems are the backbone of hotel operations. They manage critical tasks like guest check-in/check-out, room assignments, and reservation tracking. Modern PMSs integrate with other systems, offering a holistic view of hotel operations. Key features include: integrated reservation systems, online booking engines, automated guest communication, and robust reporting tools.
Revenue Management System (RMS)
Revenue Management Systems are designed to optimize revenue generation by strategically adjusting pricing based on demand and market conditions. These systems use complex algorithms to analyze historical data and forecast future trends, providing insights into pricing strategies and maximizing profitability. Key features include: demand forecasting, dynamic pricing tools, rate optimization algorithms, and revenue performance reporting.
Sales and Marketing Software
Sales and marketing software tools support marketing campaigns, manage leads, and track sales performance. These systems facilitate communication with potential guests, track campaign effectiveness, and ultimately improve conversion rates. Key features include: CRM integration, email marketing automation, social media management tools, and sales reporting dashboards.
Channel Management System (CMS)
Channel Management Systems manage the distribution of hotel inventory across various online travel agencies (OTAs), direct booking channels, and other sales platforms. These systems ensure accurate and up-to-date inventory across all channels. Key features include: inventory synchronization, commission tracking, and performance reporting.
Table: Types of Hotel Software
| Software Type | Functionality | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|
| Property Management System (PMS) | Guest management, reservation tracking, room assignment, billing, reporting | Typically tiered pricing based on features and number of users |
| Revenue Management System (RMS) | Demand forecasting, dynamic pricing, rate optimization, revenue analysis | Typically subscription-based pricing, often tied to revenue generated |
| Sales and Marketing Software | Lead management, email marketing, social media management, campaign tracking | Subscription-based pricing with varying tiers of features |
| Channel Management System (CMS) | Inventory management across multiple channels (OTAs, direct booking), commission tracking | Typically subscription-based pricing, potentially with transaction fees |
Evolution of Hotel Software
Hotel software has evolved significantly over the years. Early systems were basic and often standalone. Today, cloud-based, integrated solutions are the norm, providing real-time data and comprehensive insights. Key advancements include the integration of various software types, the increasing use of data analytics, and the growing importance of mobile-first design. The shift towards cloud-based solutions has significantly reduced the initial investment and maintenance costs, making software more accessible to smaller hotels.
Software Selection Criteria
Choosing the right hotel software is crucial for operational efficiency and profitability. A well-selected system streamlines processes, improves guest satisfaction, and provides valuable data for informed decision-making. This section delves into the essential criteria for evaluating hotel software, considering diverse factors that influence the selection process.
Selecting the ideal software solution requires careful consideration of a hotel’s unique needs and resources. Understanding the specific requirements and prioritizing features accordingly is vital for maximizing the software’s benefits.
Budgetary Considerations
A critical aspect of software selection is the budget. Hotels need to establish a realistic budget for software acquisition, implementation, and ongoing maintenance. This includes costs for licenses, training, and potential integration with existing systems. It is crucial to factor in potential future costs, like upgrades or add-ons, to avoid unexpected financial burdens. Realistic budgeting involves comparing different software packages, assessing the associated costs, and determining the long-term value proposition.
Scale of Operations
The scale of a hotel’s operations significantly influences software selection. Small hotels may benefit from simpler, more affordable software solutions, whereas large hotels require more robust systems with advanced features for managing complex operations. The number of rooms, staff, and daily transactions directly impacts the software’s required functionality.
Specific Hotel Needs
Hotels must carefully evaluate their unique needs when choosing software. Different hotels cater to different types of guests and have varying operational requirements. A boutique hotel might prioritize features like personalized guest experiences, while a budget hotel may focus on cost-effectiveness and streamlined check-in/check-out procedures. Understanding the target clientele and operational needs helps tailor the software to specific demands.
Decision-Making Factors
Several factors influence the decision-making process for choosing hotel software. These factors include vendor reputation, customer reviews, available support, and the software’s ease of use. Hotels should prioritize solutions that offer excellent customer service and responsive support.
Feature Prioritization
Prioritizing features is essential to align the software with the hotel’s unique requirements and goals. Hotels should identify the features that are most critical for their daily operations and guest experience. This involves evaluating the importance of features like room management, revenue management, or guest communication.
Integration Capabilities
Integration capabilities are crucial for seamless operation. Software that integrates well with existing systems, such as property management systems (PMS), central reservation systems (CRS), and point-of-sale (POS) systems, can minimize data entry errors and enhance operational efficiency. This integration avoids redundant data entry and ensures a cohesive flow of information across different departments.
User-Friendliness
User-friendliness is a critical factor in software selection. Software should be intuitive and easy to navigate for both staff and management. The user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) should be carefully evaluated to ensure ease of use and minimize training time. A user-friendly system contributes to higher staff productivity and reduced errors.
Comparative Analysis of Top Hotel Software Solutions
| Software | Key Features | Pricing | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software A | Advanced room management, robust reporting, seamless integration | High | Excellent data analysis, extensive customization | Steeper learning curve, potentially high implementation costs |
| Software B | Intuitive interface, user-friendly design, comprehensive reporting | Medium | Easy to learn and use, cost-effective for smaller operations | Limited customization options, fewer advanced features |
| Software C | Focus on revenue management, channel management, strong guest communication tools | High | Maximize revenue generation, improve guest satisfaction | Can be complex for smaller operations, higher upfront cost |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Detailed pricing and feature lists vary among providers. A comprehensive evaluation should involve detailed inquiries and demos.
Benefits and Advantages
Hotel software offers a multifaceted approach to enhancing operational efficiency, guest satisfaction, and staff productivity. By streamlining processes and providing comprehensive data insights, hotels can significantly improve their bottom line and guest experience. This section details the key advantages of adopting such software.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Implementing hotel software streamlines various operational tasks, leading to significant time savings and reduced errors. Automated check-in/check-out procedures, inventory management, and communication tools reduce manual effort, freeing up staff for more valuable tasks. This automation translates into substantial cost savings and increased overall operational efficiency. For example, a hotel using a property management system (PMS) can track room availability in real-time, reducing double-bookings and maximizing revenue.
Enhanced Guest Experience
Hotel software facilitates a more personalized and responsive approach to guest service. Through integrated reservation systems and guest profiles, hotels can provide tailored recommendations and services, leading to increased guest satisfaction. Personalized amenities and communication channels enhance the guest experience, increasing loyalty and positive word-of-mouth referrals. This approach is exemplified by hotels using customer relationship management (CRM) software to track guest preferences and provide anticipatory services.
Increased Staff Productivity and Workflow
Hotel software optimizes staff workflows, enabling employees to focus on tasks requiring interpersonal skills and direct guest interaction. Automated tasks such as room assignments, billing, and maintenance requests allow staff to concentrate on providing exceptional guest service. This shift in workflow enhances staff morale and job satisfaction, leading to improved service quality. For instance, a hotel using a point-of-sale (POS) system can quickly process payments and manage inventory, allowing staff to focus on guest interactions.
Quantifiable Benefits of Hotel Software
The following table demonstrates the quantifiable benefits of implementing hotel software across various operational areas:
| Operational Area | Benefit | Quantifiable Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Reservations | Reduced no-shows, improved room occupancy rates, and automated confirmations | Potential for 5-15% increase in room revenue through improved booking management and reduced no-shows. |
| Guest Services | Personalized guest interactions, proactive service recommendations, and streamlined communication channels | Improved guest satisfaction scores (e.g., Net Promoter Score) by 10-20% through proactive communication and personalized service. |
| Finance | Automated invoicing, accurate financial reporting, and streamlined payment processing | Reduced administrative costs by 10-20% through automated invoicing and streamlined payment processing. |
| Maintenance | Efficient tracking of maintenance requests, optimized maintenance scheduling, and reduced downtime | Potential for 10-15% reduction in maintenance costs and downtime through improved scheduling and management. |
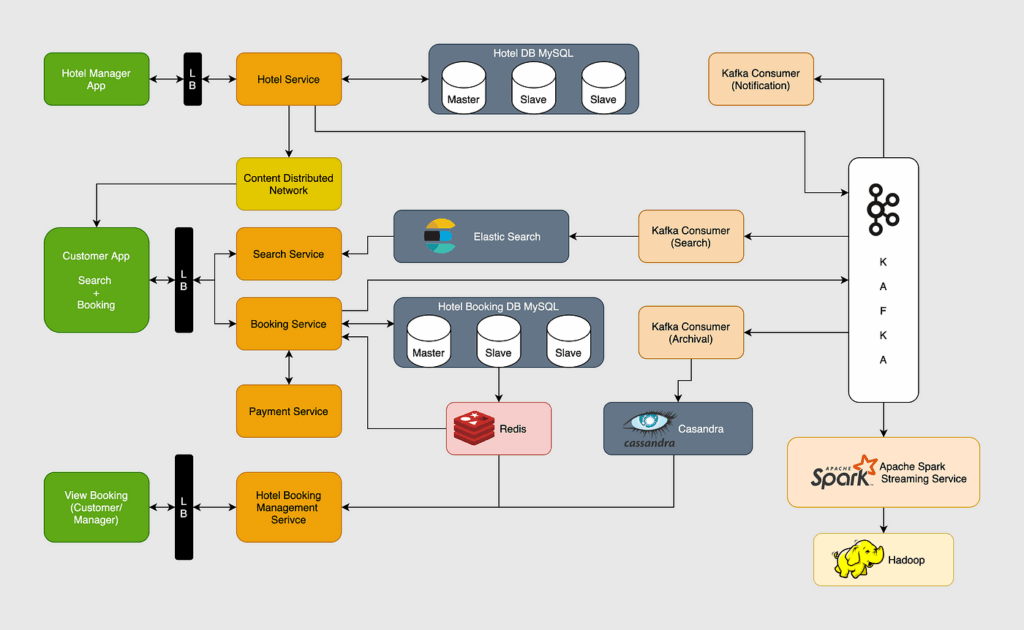
Implementation and Integration: Best Hotel Software

Source: cnyglock.com
Implementing new hotel software is a crucial step for hotels seeking to optimize operations and enhance guest experiences. A well-planned and executed implementation ensures minimal disruption and maximizes the software’s potential benefits. This involves careful consideration of existing systems, data migration strategies, and potential challenges.
The process of integrating new software with existing hotel systems is critical. A seamless integration ensures data consistency and avoids redundant manual work. A successful integration relies on meticulous planning, clear communication, and robust testing.
Implementation Steps
Implementing hotel software requires a structured approach. The process typically involves several key steps:
- Needs Assessment and Planning: This phase focuses on understanding the hotel’s specific needs and aligning the software with those requirements. A detailed assessment identifies existing processes, data flow, and future goals to ensure optimal software selection and integration. This step involves evaluating current systems, outlining desired improvements, and creating a timeline for implementation.
- System Configuration and Setup: This phase involves configuring the chosen software to meet the hotel’s unique needs. This includes setting up user accounts, defining access levels, and configuring various settings within the system. This step also involves tailoring the software to specific hotel requirements, potentially through custom integrations or configurations.
- Data Migration: This crucial step involves transferring existing data from legacy systems into the new software. Effective data migration strategies ensure accuracy and prevent data loss. A careful plan is essential, encompassing data validation, cleansing, and transformation processes. A clear understanding of the data structure and mapping between old and new systems is paramount. Consider using ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools to automate this process.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing is critical to ensure the software functions as expected and meets the hotel’s needs. Testing should cover various scenarios, including normal operations, edge cases, and error conditions. This phase identifies and addresses any bugs or issues before the system goes live. Thorough user acceptance testing (UAT) with representative hotel staff is highly recommended.
- System Go-Live and Training: The go-live stage involves deploying the software and transitioning the hotel’s operations to the new system. This phase requires comprehensive training for staff on using the new software. Detailed training materials, including tutorials and practical exercises, are vital for successful adoption. Consider staggered rollouts for smooth transitions.
- Post-Implementation Support and Maintenance: Ongoing support and maintenance are critical to ensure the software continues to meet the hotel’s evolving needs. This includes addressing any issues that arise, implementing updates, and providing ongoing technical support.
Integration with Existing Systems
Successful integration with existing hotel systems is crucial for a smooth transition. A well-defined integration strategy ensures minimal disruption to operations.
- API Integration: Leveraging Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allows seamless data exchange between the hotel software and other systems. APIs facilitate direct communication and automate data transfer, minimizing manual effort and errors.
- Data Mapping: This involves establishing clear mappings between data fields in the new software and corresponding fields in existing systems. This ensures accurate data transfer and avoids inconsistencies. Detailed documentation is essential for future reference.
- Data Validation: Implementing robust data validation checks helps maintain data integrity during integration. These checks verify the accuracy and completeness of data exchanged between systems, reducing potential errors. This often involves data quality controls and validation rules.
Data Migration Strategies
A well-executed data migration strategy is critical for a smooth transition. Data loss or errors can severely impact operations.
- Data Extraction: Carefully extract data from the old system using appropriate tools and techniques. Consider using database migration tools to automate this process, minimizing manual errors. The extraction process should consider data volume and complexity.
- Data Transformation: Data transformation involves converting the extracted data into the required format for the new system. Careful mapping and validation steps are needed to ensure data accuracy and integrity. This often involves scripting or specialized tools.
- Data Loading: Loading the transformed data into the new system using appropriate methods and tools. This step involves verifying data accuracy and completeness after loading. Consider incremental loading strategies to minimize disruption to ongoing operations.
Challenges and Solutions
Implementing new hotel software can present various challenges. Proactive planning and problem-solving are crucial.
- Resistance to Change: Staff resistance to adopting new systems can hinder implementation. Effective communication and training strategies can address this issue. Emphasize the benefits and value proposition for staff.
- Data Inconsistencies: Data discrepancies between legacy and new systems can impact integration. A meticulous data cleansing and validation process can mitigate these issues. Detailed data profiling and analysis can reveal inconsistencies.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the new software with existing systems can be complex. A thorough analysis of system dependencies and APIs can simplify the process. Consider hiring expert consultants if necessary.
Hotel Software Trends
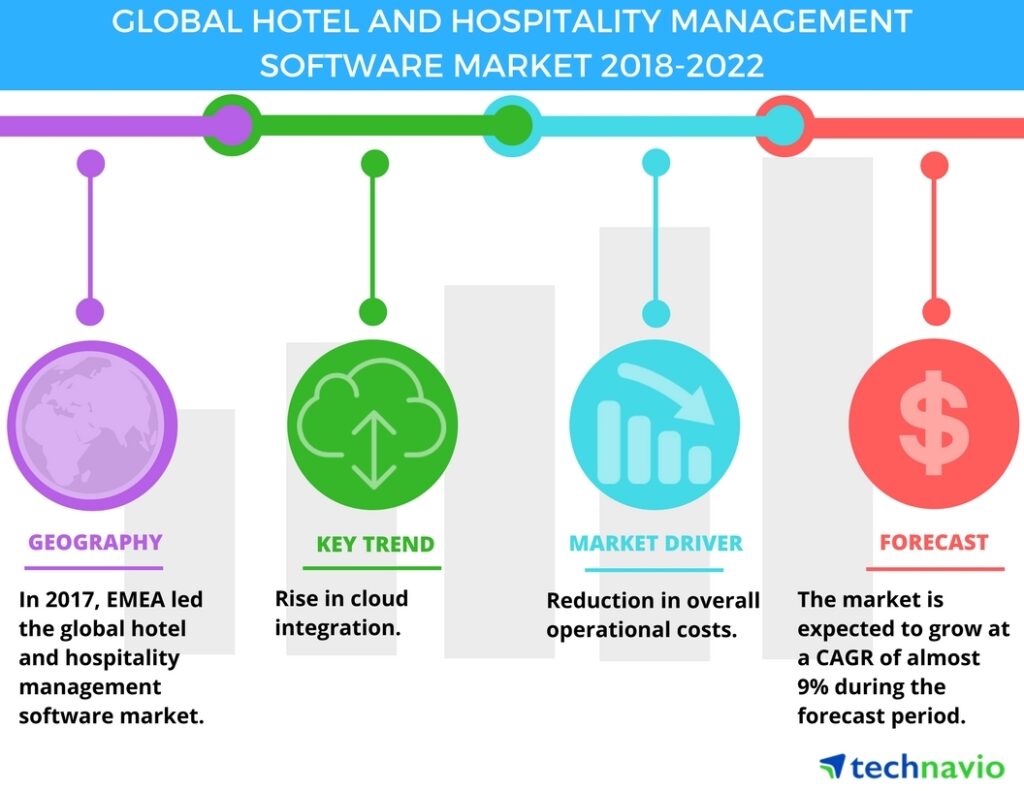
The hotel industry is undergoing a rapid digital transformation, driven by evolving guest expectations and technological advancements. Hotel software is at the forefront of this change, constantly adapting to meet the demands of a modern, tech-savvy clientele. This evolution presents both opportunities and challenges for hoteliers seeking to optimize their operations and enhance the guest experience.
Emerging Trends in Hotel Software
Several key trends are reshaping the landscape of hotel software. Cloud-based solutions, AI integration, and personalized guest experiences are driving innovation, while enhanced security measures and data analytics capabilities are crucial for long-term success. The adoption of these trends is not just about technological upgrades, but a strategic shift in how hotels manage operations, engage with guests, and achieve profitability.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based hotel software offers significant advantages, including scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Hotels can access their data and manage operations from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and increased flexibility. Furthermore, cloud solutions often come with automatic updates and maintenance, reducing the burden on IT staff and ensuring smooth operations. This accessibility and scalability are especially beneficial for smaller and medium-sized hotels, allowing them to compete effectively with larger establishments.
AI Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming hotel operations. AI-powered chatbots can handle guest inquiries, personalize recommendations, and streamline check-in/check-out processes. Predictive analytics tools can assist with revenue management, forecasting demand, and optimizing pricing strategies. Moreover, AI can analyze guest data to tailor marketing campaigns and enhance customer service, leading to a more personalized and engaging experience. For instance, AI-driven systems can proactively address guest needs, such as recommending nearby attractions based on preferences or suggesting room upgrades based on historical booking patterns.
Importance of Staying Updated
The hotel industry is highly competitive. Hotels that fail to adapt to technological advancements risk losing market share and falling behind competitors. Staying abreast of new trends in hotel software ensures hotels can effectively leverage technology to improve efficiency, enhance guest satisfaction, and optimize revenue generation. Continuous learning and adaptation are vital for long-term success in this dynamic environment.
Predictions for Future Development
Future hotel software will likely integrate more sophisticated AI capabilities, providing even more personalized experiences. The emphasis will shift towards seamless and intuitive user interfaces, making operations more efficient and user-friendly. Blockchain technology may play a role in enhancing security and transparency in transactions, while the Internet of Things (IoT) will further automate and optimize hotel operations. For example, smart room controls integrated with AI will anticipate guest needs, enhancing comfort and convenience.
Growth and Adoption Rates of Hotel Software
| Software Type | Growth Rate (2020-2025) | Adoption Rate (2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Property Management Systems (PMS) | 15% | 85% |
| Central Reservation Systems (CRS) | 12% | 70% |
| Revenue Management Systems (RMS) | 18% | 60% |
| Guest Relationship Management (CRM) | 20% | 75% |
| Online Booking Engines (OBEs) | 10% | 90% |
Note: Growth rates and adoption rates are estimations based on industry reports and market trends. Data may vary based on specific region or hotel size.
Case Studies and Examples
Implementing hotel software successfully hinges on understanding how it can address specific operational challenges and enhance revenue streams. Analyzing real-world examples provides valuable insights into the benefits and potential pitfalls of various software solutions. This section will present case studies of hotels that have effectively leveraged hotel software to improve their performance.
This section will explore how different hotels have employed specific software to overcome challenges, optimize operations, and ultimately achieve positive outcomes. We will analyze the specific impacts on operational efficiency and revenue generation, showcasing successful strategies for enhancing hotel performance.
Successful Hotel Software Implementation: Case Study 1, Best hotel software
This case study focuses on a mid-sized hotel chain known for its commitment to personalized guest experiences. They recognized a need to streamline their booking process and improve customer service efficiency. They chose a cloud-based property management system (PMS) that integrated seamlessly with their existing online booking engine.
- The hotel initially faced challenges in managing reservations across multiple channels, leading to inconsistencies and delays in communication with guests.
- The new PMS automated reservation management, providing real-time updates and centralized access to information for all staff members.
- This resulted in a 20% reduction in reservation errors and a 15% improvement in guest satisfaction scores, as measured by surveys and online reviews.
- The software also facilitated better inventory management, leading to improved room occupancy rates and increased revenue.
Successful Hotel Software Implementation: Case Study 2
A luxury boutique hotel sought to enhance guest experiences and increase revenue by providing a superior level of personalized service. They implemented a sophisticated customer relationship management (CRM) system integrated with their PMS.
- The hotel previously struggled with tracking guest preferences and historical data, hindering the ability to tailor services to individual needs.
- The CRM allowed the hotel to create detailed guest profiles, capturing preferences, past stays, and special requests.
- Staff were trained to access and utilize the CRM information, resulting in proactive service and personalized recommendations.
- The hotel observed a 10% increase in repeat guest bookings and a 12% rise in average daily rate (ADR) due to enhanced guest satisfaction.
Successful Hotel Software Implementation: Case Study 3
A budget-friendly hotel aimed to optimize its operational costs and increase efficiency. They implemented a comprehensive revenue management system (RMS) to manage pricing strategies dynamically.
- The hotel previously relied on manual pricing adjustments, resulting in missed opportunities for maximizing revenue and inefficient resource allocation.
- The RMS automated pricing strategies based on demand, competitor pricing, and other factors, ensuring optimal pricing in real-time.
- This automation significantly reduced manual workload, leading to a 15% increase in revenue per available room (RevPAR) and a 10% decrease in operational costs.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the best hotel software is a powerful tool for modern hospitality. By understanding the various types, selection criteria, and benefits, hotels can optimize their operations, enhance guest experiences, and boost profitability. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the landscape, covering everything from initial software selection to implementation and ongoing trends. Successful implementation requires careful planning, integration, and a willingness to adapt to evolving technological advancements. Ultimately, choosing the right software is an investment in the future of your hotel, and this guide equips you with the knowledge to make that critical decision.